At Bushings & Bars, we distribute bushings/plain bearings, material bars, and other engineering components direct from US-based manufacturers to our valued customers. One of our core product lines is PTFE and nylon bushings and thrust washers.
VIEW OUR CATALOG
What Are Bushings and Thrust Washers?
Bushings—also referred to as plain bearings, plain bushings, or sleeve bearings—are machined or formed components designed to reduce friction, improve efficiency, and reduce vibration and noise between a rotating or sliding shaft and the supporting structure.
Thrust washers – are specially designed flat washers that are located between a rotating surface and a stationary component. They can be used as a standard washer or they can be used to support the axial load or side to side motion on a shaft and prevent movement along that shaft. The thrust washer helps to provide a surface on to which a bearing is supported.
Properties of PTFE and Nylon
Bushings and thrust washers are typically made from metal or plastic material. Depending on the intended use, plastic or non-metallic variants can provide a number of advantages over metal variations. For example, metal bushings and thrust washers often require external lubrication, which can be difficult or detrimental in certain applications. Bushings and thrust washers made from certain plastics—such as PTFE or nylon offer self-lubricating properties, which make them a simpler and easier solution.
PTFE and nylon are just two of the plastics commonly used in the manufacture of bushings and thrust washers. Each of these thermoplastic materials exhibits unique properties that make it suitable for different applications. Below, we highlight some of the key characteristics of each material to help you determine which one best suits your bushing and thrust washer needs.
 PTFE vs. Nylon
PTFE vs. Nylon
As indicated above, PTFE and nylon have many similarities, including elevated mechanical strength and low coefficient of friction. These shared properties make them suitable for use in many of the same applications, including in the aerospace, automotive, construction, defense, and plumbing industries. However, the materials also have some differences, including with regard to their operating temperatures, self-lubricating properties, electrical conductivity, chemical reactivity, water interactivity, and cost. These and other distinct properties are important to keep in mind and should be carefully reviewed and considered to ensure that the right material has been selected for the application. As is common for most self-lubricating bearing applications, it’s generally a good idea to initially apply a light grease or oil to the application to facilitate the initial break-in of the bearing.
For example:
- PTFE is non hygroscopic // hydrophobic, while nylon is hygroscopic // hydrophilic. The difference in how the two materials interact or do not interact with water makes PTFE a better choice than nylon for high-moisture applications that require greater lubrication characteristics or dimensional stability.
- PTFE has a typical max operating temperature of around 550° F, while nylon has a typical max operating temperature of around 220° Care must be taken into account for the effects of temperature on bearing applications. PTFE has a higher operating range than nylon so it typically better suited for applications involving extreme temperatures.
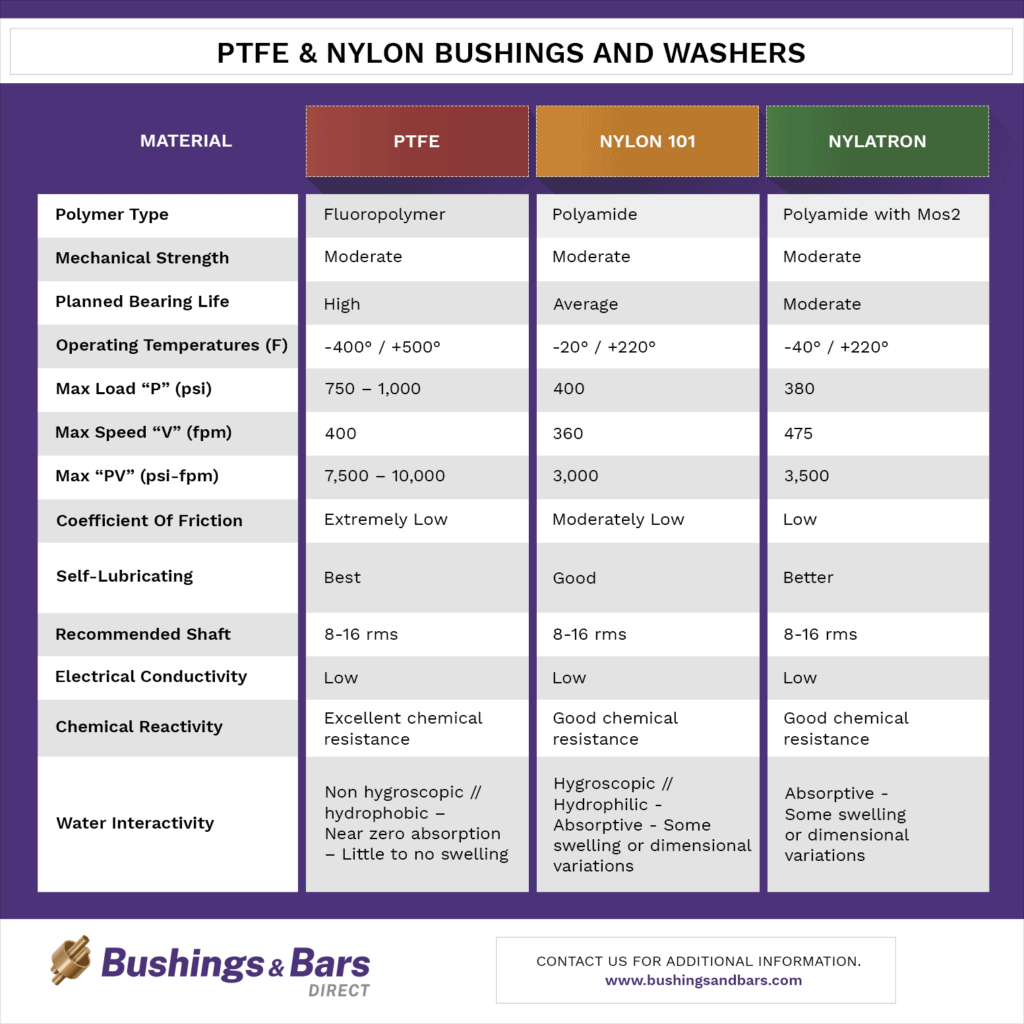
| Material | PTFE | Nylon 101 | Nylatron |
|
Polymer type |
Fluoropolymer | Polyamide | Polyamide with Mos2 |
|
Mechanical strength |
Moderate | Moderate | Moderate |
| Planned bearing life | High | Average | Moderate |
| Operating temperatures (F) | -400° / +500° | -20° / +220° | -40° / +220° |
| Max Load “P” (psi) | 750 – 1,000 | 400 | 380 |
| Max Speed “V” (fpm) | 400 | 360 | 475 |
| Max “PV” (psi-fpm) | 7,500 – 10,000 | 3,000 | 3,500 |
| Coefficient of friction | Extremely Low | Moderately Low | Low |
| Self-lubricating | Best | Good | Better |
| Recommended shaft | 8-16 rms | 8-16 rms | 8-16 rms |
| Electrical conductivity | Low | Low | Low |
| Chemical reactivity | Excellent chemical resistance | Good chemical resistance | Good chemical resistance |
| Water interactivity | Non hygroscopic // hydrophobic –
Near zero absorption – Little to no swelling |
Hygroscopic // Hydrophilic –
Absorptive – Some swelling or dimensional variations |
Hygroscopic // Hydrophilic –
Absorptive – Some swelling or dimensional variations |
** This information is intended to be a general reference guide and does not make any application specific recommendations
VIEW OUR CATALOG
Nylon and PTFE Bushings and Washers from Bushings & Bars
Plastic bushings and thrust washers can offer a variety of advantages over their metal counterparts, such as better lubrication. If you’re looking for quality nylon and PTFE bushings and thrust washers, Bushings & Bars has you covered. For more information, please view our catalog or contact us today.